Summary: Periodontal disease is a significant dental concern characterized by the inflammation and infection of the tissues surrounding the teeth. This article delves into the intricacies of periodontal disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, and effective treatments. By understanding this condition, individuals can take proactive measures to maintain optimal oral health. We examine various risk factors, discuss notable symptoms that indicate the presence of the disease, and outline effective treatment strategies ranging from professional cleaning to surgical options. Education about periodontal disease is crucial, as it can lead to severe health implications if left untreated. Ultimately, this guide aims to empower readers with the knowledge necessary to manage their oral health effectively.
1. Causes of Periodontal Disease
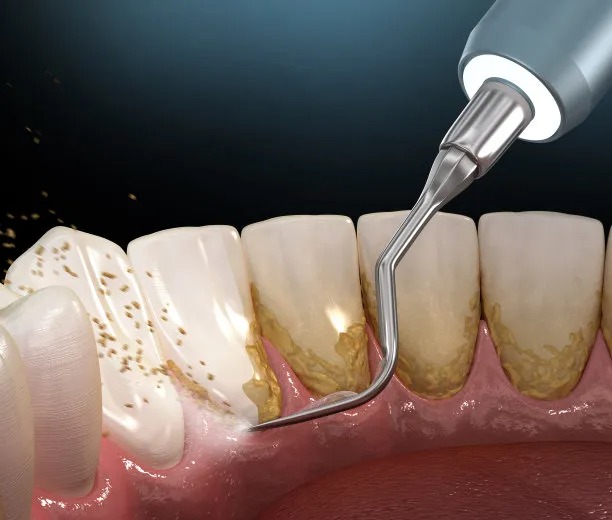
Periodontal disease often stems from poor oral hygiene practices that encourage plaque buildup on teeth, leading to inflammation. Plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, can harden into tartar if not regularly removed. This accumulation can irritate the gum tissue, resulting in gingivitis, the early stage of periodontal disease. Neglecting regular dental cleanings exacerbates this situation, allowing bacteria to proliferate.
Other significant risk factors include smoking and tobacco use. Research shows that smokers are more likely to develop periodontal disease due to the detrimental effects of nicotine on blood flow to the gums. Reduced blood supply impairs healing and increases the susceptibility to infections.
Underlying health conditions also play a crucial role in the development of periodontal disease. Conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune disorders disrupt the bodys ability to combat infections. Individuals with compromised immune systems may find it challenging to fend off gum disease, making regular dental visits even more vital.
2. Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
Identifying the symptoms of periodontal disease early can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Common signs include swollen or bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing. Patients may also notice persistent bad breath, which can result from bacteria accumulating in the mouth and causing infections.
The condition can progress to more serious symptoms as it advances. Receding gums, which result in longer-looking teeth, occur as periodontal disease progresses. Additionally, individuals might feel discomfort or pain when chewing, signifying potential deterioration of the supportive structures around teeth.
In its most severe form, periodontal disease can lead to tooth mobility or even tooth loss. This stage highlights the importance of regular dental check-ups, as early intervention can prevent the progression of symptoms and the overall disease.
3. Effective Treatments for Periodontal Disease
Effective management of periodontal disease typically begins with professional dental cleanings. These cleanings remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line, reducing inflammation. Dentists often recommend scaling and root planing, a deep cleaning procedure that smooths the root surfaces to encourage healing.
Medications can also play a significant role in treatment. Topical antibiotics may be prescribed to control bacterial infection, while oral antibiotics may be indicated for more severe cases. Antimicrobial mouth rinses can help in reducing bacteria and promoting healing.
In instances where non-surgical treatments appear ineffective, surgical interventions may be necessary. Procedures like flap surgery or bone grafting can restore gum health and support lost bone structure. It’s crucial for patients to adhere to post-treatment care to ensure optimal healing and prevent recurrence.
4. Maintaining Optimal Oral Health
Preventive measures are vital when it comes to maintaining oral health and preventing periodontal disease. Regular brushing with fluoride toothpaste and daily flossing can significantly reduce plaque buildup. Additionally, individuals should avoid tobacco products and limit sugary snacks that promote cavity formation and gum disease.
Routine dental visits, ideally every six months, are essential. These appointments enable early detection of periodontal issues before they become severe. Dentists can provide customized advice about home care practices tailored to individual needs.
Finally, a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports gum health. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provide essential nutrients that strengthen both teeth and gums, contributing to overall oral well-being.
Summary: Understanding periodontal disease is integral for anyone seeking to maintain their oral health. By recognizing its causes, symptoms, and effective treatments, individuals can take proactive steps toward prevention and management. Staying informed empowers patients to seek timely dental care, minimizing their risks and promoting their overall health.
This article is compiled by Vickong Dental and the content is for reference only.


